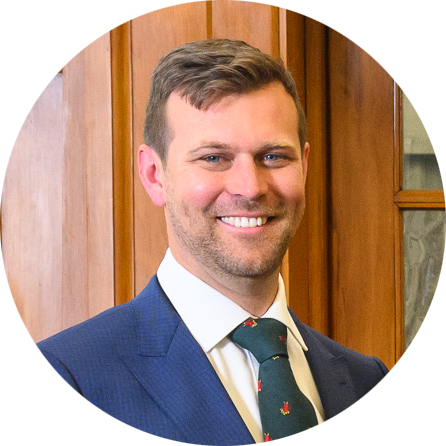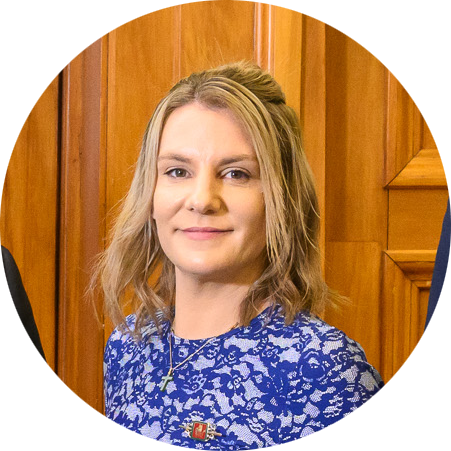
Phillip Weir, 2020 Nuffield Scholar.
In February, Nuffield Scholar and Waikato farmer Phillip Weir was appointed an associate board member of the Agricultural and Marketing Research and Development Trust (AGMARDT).
The AGMARDT associate trustee position gives emerging leaders an opportunity to learn, develop and supports AGMARDT’s mission to nurture people and ideas and in putting people at the heart of what it does, while focusing on the things that create the most impact.
In a recent Farmers Weekly article Phillip said, “I’m looking forward to supporting fantastic people who have great ideas that will both change the future of New Zealand Food and Fibre production and will be essential in its future.”
Phillip is also standing for election to Beef + Lamb New Zealand’s Board, Northern North Island region. We’re sure Phillip would appreciate our support.
Phillip and his wife Megan farm dairy-beef bulls and sheep on the side of Mt Pirongia, Waikato.
Phillip’s profile for the voting can be found here.
You can also learn more on how to vote at the B+LNZ contact details below.
Candidate profiles and voting papers should be with voters (from Northern North island voting area) by now as part of the annual meeting voting pack. All registered farmers elsewhere across the country should also have received a meeting pack.
In a recent Farmers Weekly article Phillip said, “We have debt. We have kids. We shift bulls. I am not a professional director. I’m proud of our Ballance Farm Environment Award, my Nuffield Scholarship and industry contributions as Farmer Council Chair.”
About the voting process.
The director election and postal and electronic voting close March 13.
If you’ve previously received annual meeting materials from B+LNZ you’re already on the electoral roll.
However if you’re not sure and want to check, you can:
call B+LNZ on 0800 BEEFLAMB (0800 233 352)
or email enquiries@beeflambnz.com
Vanessa Thomson, 2023 Kellogg Scholar. Donna Cram, 2023 Value Chain Innovation Programme.
Vanessa Thomson, did the Kellogg Rural Leadership Programme in 2023 and is a working mum with a young family, who sharemilks with her husband on two farms in the Waikato. She is also an ex-lawyer and currently the contract manager for DairyNZ.
In 2022 Vanessa received a scholarship to the Kellogg Programme through Dairy Women’s Network (DWN) and in a recent interview with DWN said, “It’s been a life-changing opportunity for me, and I am so grateful for the network that I have made through Kellogg, and the tools that it has given me. I am excited for the future, and what my leadership journey might bring.”
Check out the full article here.
Vanessa’s Kellogg research ‘The effectiveness of psychosocial services available to farmers following adverse events’ examined who the stakeholders are in the rural psychosocial ecosystem, how farmers interact with these stakeholders, and how these interact together. The research aimed to understand the challenges of delivery of effective psychosocial services.
In 2023 Donna Cram won the Fonterra Dairy Woman of the Year. Donna chose to use some of the scholarship to attend Rural Leaders’ Value Chain Innovation Programme, instead of the Kellogg Programme.
Donna has said that just as much was learned from the deep, insightful and honest bus and evening meal discussions with other participants on the Value Chain Programme, as from the rural leaders who welcomed them into their businesses.
Applications close soon on 29 February.
More information about the award, click here.
To apply or nominate, click here.
James Parsons, 2008 Nuffield Scholar.
James Parsons is co-owner of Matauri Angus beef stud and the 600 hectare Ashgrove Farm, near Dargaville. He has been trialling Halter collars on breeding cows and heifers for the past three months.
You may have seen James on a recent brand ad for Halter. You can have a look here.
James and his family’s sheep and beef farming business, Ashgrove Ltd, breeds and provides sheep and beef genetics to clients throughout the country. He is also former chairperson of Beef + Lamb New Zealand and is a board member of AgFirst Northland and chair of Wools of NZ.
In a February 19 article in Farmers Weekly, James shared his thoughts on what he sees as a game-changer for hill country farming.
Check out more in the article around cattle adaptability, grazing pressure, and calf growth rates.
Kylie Leonard, 2023 Nuffield Scholar.
Kylie was recently interviewed by the Pathways to Dairy Net Zero initiative (P2DNZ).
Founded in 2021, during Climate Week, P2DNZ is dedicated to reducing dairy’s greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions.
P2DNZ is providing insights and solutions to help Kylie overcome any farm challenges and more broadly accelerate climate action throughout the dairy industry.
You can read the interview here.
Carlos Bagrie, 2024 Nuffield Scholar.
Carlos’s innovative and unique approach to farming, the transformation of waste into a viable resource, as well as a few impressive side projects, were the subjects of a not-so-recent interview with REX host Dominic in late December.
Carlos’s energy and passion for what he does is infectious and FYI, his innovation doesn’t stop at zero-waste solutions. There are plenty of great ideas being realised at Royalburn Station with his wife and family. This podcast is well worth a listen – especially if you need a good dose of positivity.